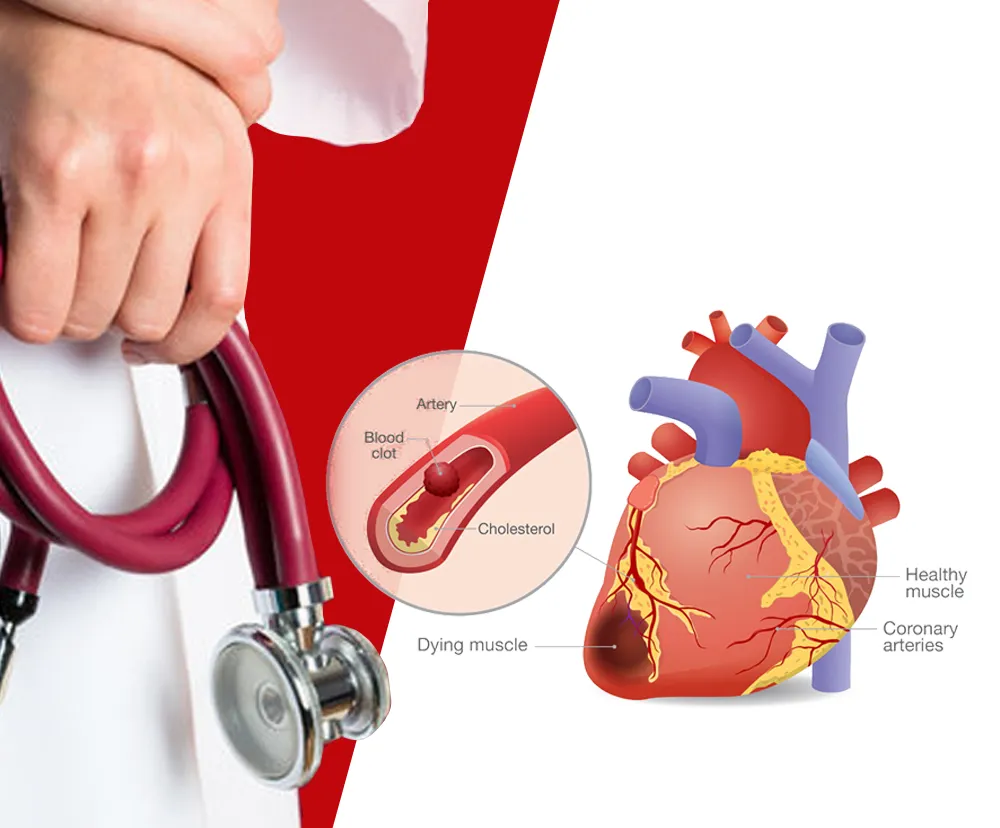
What is the Main Reason of Heart Attack among Young Adults?
What is the Main Reason of Heart Attack among Young Adults?
- What is the reason of heart attack in young age?
- What is the difference between congenital and inherited?
- Is it possible to detect heart attack risk or conditions through symptoms?
- What are the samples that I need to provide for genetic testing for heart attack risk?
- What are the genetic tests for heart attack risk?
Introduction
There is no specific age group for heart attack, as more and more young adults have experienced a heart attack. However, there are certain typical trends that are used to indicate the average age of people who have had a heart attack. For men, the average age for the first heart attack is around 65 years old, and for women it is around 72 years. However, recent reports offer proof that young adults below the age of 45 are also now prone to heart attacks. These are not attributed to any single reason of heart attack but are typically due to a combination of reasons.
What is the reason of heart attack in young age?
Multiple factors are responsible for a heart attack in young adults. Before we look at the reason of heart attack, here is an example worth noting. Saif Ali Khan, the famous Bollywood star had a heart ailment at the age of 36, due to reduced blood flow to the heart. He survived and is now leading a normal life, thanks to timely treatment and post-treatment care. Testing of the condition at the right time played an important role in determining the actual cause.
Let’s look at the different reasons that could cause a heart attack among young people. These are usually different from reasons for heart attacks in older adults.
- Genetic reasons – This is a reason of heart attack among young people and older adults as well. This is attributed to a family history of heart disease. This considerably increases future or lifetime risk of heart attack, even if other contributing factors are absent.
- Specific conditions that run in the family – One possible condition is familial hypercholesterolemia that is known to end up with high cholesterol levels.
- Smoking – This is recognized as a major risk or reason for heart attack among young adults.
- Hyperglycemia – If you have abnormally high levels of blood sugar, you are at risk of developing a heart disease.
- Hypertension – This is often not detected, until it is too late. Unregulated high blood pressure levels will cause extensive damage to the arteries and heart. This develops gradually and silently, and is often detected when considerable damage is done.
- Obesity – If your weight is in the category of obesity or excessive body weight, this could result in putting you are increased risk of heart disease.
- Cholesterol – When your cholesterol levels are high, it can result in buildup of plaque and cause partial or complete blockage of your arteries.
- Underlying conditions – Certain existing inflammatory and autoimmune conditions are also a reason of heart attack. This includes lupus and kawasaki disease.
- Congenital defects – People born with structural heart problems are more prone to heart attack risk.
What is the difference between congenital and inherited?
It is necessary to know the distinction between congenital and inherited, cited as a reason of heart attack above. Congenital refers to conditions that may be present in a person at birth, as some kind of defect. Inherited conditions refer to defects that are passed down the family through genes. These genetic mutations run in the family exposing many members to a similar disease.
Is it possible to detect heart attack risk or conditions through symptoms?
Yes, it is possible to detect risk of heart attack through certain tell-tale symptoms. Awareness of the reason of heart attack helps to go in for timely screening and preventive treatment. This will help to reduce the risk considerably and also reduce the effect of heart attacks in the eventuality of an occurrence.
Symptoms can indicate the conditions that contribute to the risk of heart attack. Genetic testing can identify many issues that will later contribute to the risk of heart attack. For instance, genetic testing can determine if you have any genetic mutations or variants due to congenital defects. Similarly, genetic testing will also help to determine if you have any inherited conditions that can develop into a risk or reason of heart attack.
What are the samples that I need to provide for genetic testing for heart attack risk?
The samples that you need to provide for genetic testing for heart attack risk could be either saliva or blood sample, depending on the test. Drawing of these samples do not require time and are carried out in the laboratory. DNA is extracted from the samples; the findings are then analyzed and reports generated. These reports will offer a clear risk score indicating if you have any condition that could be a reason of heart attack.
Presently, there are advanced genetic testing facilities in Tamilnadu to screen for risk of heart attack. This will help you understand if you have any conditions that will become a reason of heart attack in the future. Upon identifying this lifetime risk or a future risk of heart attack, you can then seek suitable treatment to prevent or mitigate the risk. This could be through lifestyle changes, medications and procedures wherever necessary.
What are the genetic tests for heart attack risk?
The following tests are carried out to check for risk of heart attack. The reports of these tests are always used along with other clinical data, observations and medical records to determine risk and the most suitable treatment approach.
- Polygenic Risk Scores – This is an aggregate score of the effects of multiple genetic variants and help determine your overall genetic risk of ending up with heart disease.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms – This test looks for changes on chromosome 9 which are linked to risk of coronary artery disease.
- Specific Genes – This test looks for changes in the APOE gene, that is linked to risk of heart disease.
- Lipid – This test looks for changes in the LPA gene that impacts lipoprotein levels. Thiis belongs to the category of LDL cholesterol that poses a risk of heart disease.
- Inflammation – This test looks for changes in the CRP gene, related to inflammation and risk of cardiovascular issues, when chronic.
These tests help determine your risk of heart attack, and based on the assessment, you can then take suitable, recommended remedial measures.
Medically Reviewed by
Dr.Rajasekar Cardiologist
Dr. Rajasekar is a cardiologist in Chennai, with extensive experience in the field. He completed his MBBS from Madurai Kamaraj University, followed by an MD in General Medicine and a DM in Cardiology from The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University (TNMGRMU).
Related Blogs :
Why You Need To Start Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Slide HeadingLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.Click Here Previous Next What is the main information...


Life Saving Tips on how to stop Heart Attack
Introduction How to stop a heart attack in 30 seconds? Why time is of utmost importance? How to stop heart attack if you see signs of it...

Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) from the University of Delhi Experience : Dr. Srinivasan is an experienced pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from the University of Delhi and over 12 years in the field. She has worked extensively in clinical and community pharmacy settings, focusing on patient care, medication management, and drug safety. Dr. Srinivasan also contributes to health and wellness publications and serves as a consultant for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare organizations. Her expertise spans clinical practice, pharmaceutical writing, and regulatory affairs.