What is leukemia?
What is leukemia?
Introduction
Cancers are of several types; each differs from the other due to many reasons. The key reasons include the site at which cancers develop, stage of the disease, how fast is the condition spreading, causes, etc. Cancers are essentially autoimmune conditions. These can occur at any age, and is common among both genders. The medical discipline that offers care to cancerous conditions is called oncology. There are multiple sub-types of oncology such as chemotherapy, radiation oncology, surgical oncology, etc.
What is meant by leukemia?
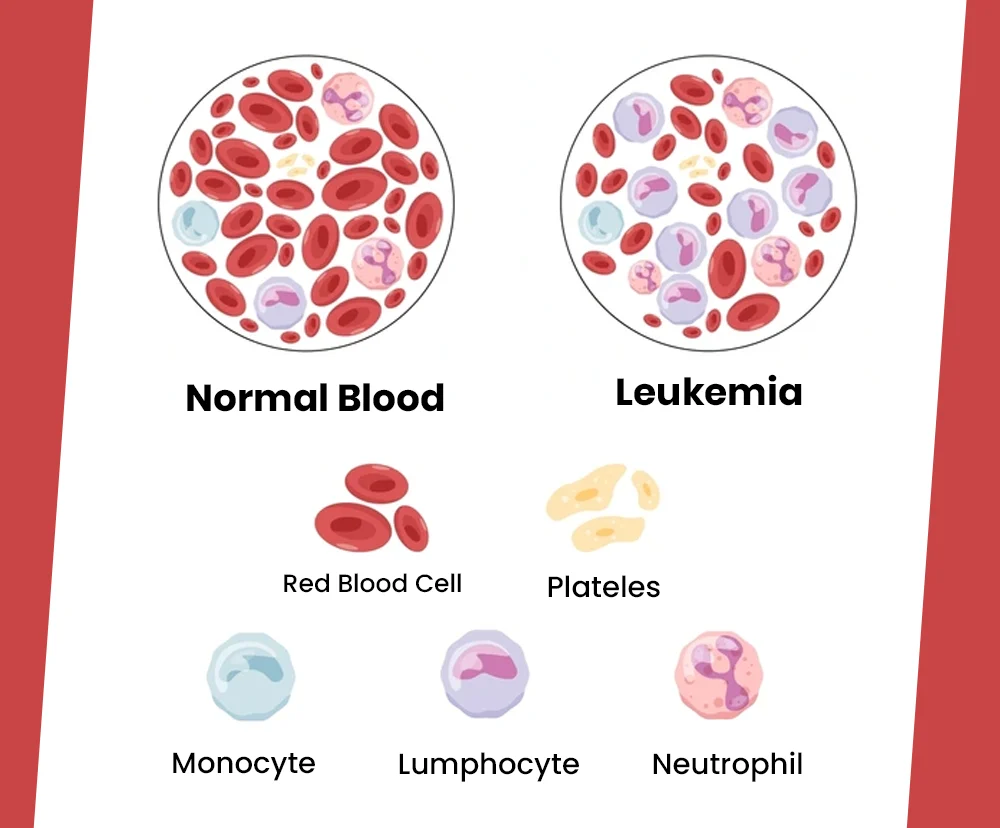
Leukemia refers to a cancerous condition of cells in your blood. This conditions often begins at the marrow – this is the place where blood cells are born. Your marrow is where young blood cells – that eventually become white cells, red cells as well as platelets take shape. Each blood cell has a function to do; for instance – red cells supply oxygen to organs and tissues; white cells protect your body from risks of infections while platelets enable clotting of blood and arrest bleeding.
Incidence of leukemia leads to your body making a larger number of blood cells; this is an abnormal condition. Of all the three types of cells, white cells tend to be more vulnerable to leukemia. If left unchecked, abnormal growth of cells may overcrowd your circulation system. In this process, your normal cells may slowly lose their ability to function properly.
Leukemia is of different types. Based on the blood cells the condition affects, leukemia can affect myeloid cells and lymphocytes. Of these myeloid cells are younger cells which eventually become white cells, red cells and platelets. Lymphocytes are a kind of white cells in blood.
Depending on how they leukemia grows and spreads, this condition can either be acute or chronic. Of these, chronic leukemia grows very slowly; it turns into an irreparable condition if left untreated. Acute form of leukemia is capable of growing very fast. This too turns worse when left without treatment.
Notwithstanding the above, key types of this blood condition are – acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Of these, acute myeloid leukemia is quite common among elderly people; however, it can also affect teens as well as children. Acute lymphocytic leukemia is a condition that affects younger adults and children; there are instances wherein grown-ups / adults have also witnessed it.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is the most commonly-occurring condition among grown-ups. People in their 30s and 40s are more likely to get it. Leukemia is diagnosed by the use of different investigative procedures. Tools used for proper diagnosis are: a thorough physical examination, proper understanding of your clinical history, ordering a panel of lab-tests like Full Blood Count (FBC), tests done on samples of your bone marrow, tests to assess changes in your chromosomes and in genes, etc.
Apart from the above, your oncologist may order a few more tests to check if cancerous conditions have spread to other tissues or organs. These additional tests are imaging-based examination, and puncture of lumbar to take a sample of your cerebrospinal fluid.
Leukemia is treated based on its type, how severe is your cancer, age your wellbeing and presence of other diseases – if any. Commonly offered treatments are radiation therapies, chemotherapy, chemotherapy along with transplantation of stem cells, targeted therapies, and chemotherapy wherein medications are used to fight specific cells and thus not harm your healthy cells.
Symptoms of leukemia
Leukemia shows up through multiple symptoms and signs. No two types of leukemia show the same kind of symptoms. Also, symptoms do not show up at all instances. At times, there may be only one sign; if it is causing you discomforts, it is a good practice to consult with your physician.
Common signs of leukemia are: being tired for most part of the day and you do not see improvements even after taking rests; frequent spells of bleeding / bruising and bleeding spells take longer time to get arrested; getting infected more often – with each episode turning severe and longer.
Signs also include an increase in body temperature; an inexplicable loss of body weight; inflammation of lymph nodes – especially in your armpits and neck region; respiratory problems like panting or grasping for breath, and being under a spell of malaise for long.
Other possible signs of leukemia include: a slowdown in your metabolic rate, a marked decrease in your appetite levels, a splitting headache or getting migraines more often. Leukemia is also capable of causing anaemia wherein your count of red cells sees a drastic drop. You can detect incidents of anaemia if you are experiencing persistent spells of fatigue, turning dizzy, pain in your chest region and paleness of skin.
Onset of leukemia may also affect blood cells that enable clotting. These cells are called platelets. Dysfunction of platelets may show-up as formation of purple or red-colored spots on your skin – triggered by internal bleeding underneath it, traces of blood in stools, darkened or tarried stools – caused by internal bleeding in the gut, increased discharge of blood during menstrual periods among women, difficulties to move your body – due to internal bleeding in your brain.
Some people have reported profuse sweating during night hours or sweats during bedtime that drench them. Leukemia may also cause your liver or spleen to get enlarged. You can sense such a swelling through pains in your tummy or underneath your ribcage – especially, on ribs of your left side. You may also feel very full after eating very small amounts of foods.
Leukemia is also capable of causing pain in your bones. This is observed when cancerous cells accumulate in your marrow. These painful conditions may make you limp or avoid walking altogether.
Symptoms of an acute version of leukemia involve a very high-count of white cells in your blood. This can make your sick, and is often treated as an emergency condition. Your sickness can manifest as neurological problems like convulsions, blurring of eyesight, being in a confused frame of mind, loss of coordination and lapses in motor skills. Some have developed respiratory conditions such as wheezing, being choked, other such breathing difficulties, etc.
Causes of leukemia
The actual causes behind the onset of leukemia are largely unknown. Research done on this blood condition indicates environmental as well as genetic triggers as the two likely causes. It is widely believed that leukemia is caused when your cells in the blood are mutated at the DNA or genetic level. Each cell is instructed by its DNA as to how it needs to act. It is your DNA which informs at what growth rate your cells need to grow, and at what time they need to die. In case of leukemia, your cells in the blood continue to multiply and also divide in an abnormal fashion.
When such unchecked growth occurs, your body produces very large amount of blood cells. Over a period of time, such abnormally-growing cells outnumber your normal cells in the bone marrow. This causes a significant reduction in healthier cells in your blood. Drop in healthy cells is observed across red cells, white cells as well as platelets
What causes blood cancer?
Leukemia, myeloma and lymphoma are the three most common forms of blood cancers. These cancers are triggered by changes occurring inside DNA of your blood cells. These can occur at any given point in time of your lifespan. A few forms of blood cancers may affect teens as well as children. The typical signs of blood cancers are quite different between grown-ups and children.
Blood cancers can be treated by various approaches depending on the type of your blood condition, the stage of your blood-condition and your age; these determine the treatment approach(es) taken. Commonly administered treatments for blood cancers are immunotherapies, targeted therapies, radiation therapy, chemotherapy either with or without transplantation of stem cells.
If the cancerous condition is growing very slowly, your doctor may not start treating you immediately. He / she may adopt a wait-and-observe strategy before commencing treatment. If you are diagnosed with cancers of blood, it is essential to know the prognosis as well.
Prognosis is a factor of outcomes of lab tests, your overall wellbeing, stage at which your cancer has been diagnosed at, etc. If your caregiving team decides to treat with chemotherapy, you are advised to adhere to all instructions of your caregiver – all through the treatment plan. During the course of treatment, if you get infected or are experiencing tiredness, extreme levels of fatigue or spells of weakness, consult with your treating oncologist without any further delay.
Related Blogs :

Leukemia Blood Test
Leukemia Blood Test Introduction Blood test for leukemia Leukemia diagnosis blood test Leukemia blood test results Leukemia cancer CBC blood test results Leukemia positive cancer blood test...

Chronic myeloid leukemia
Chronic myeloid leukemia Introduction Chronic myeloid leukemia ICD 10 What is chronic myeloid leukemia? Chronic myeloid leukemia symptoms Chronic myeloid leukemia treatment Introduction Tissues of the marrow...

Education: Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm) from the Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS), Mumbai Experience: Agarwal is a seasoned pharmacist with over 7 years of experience in the pharmaceutical field. She has worked in various settings, including hospital pharmacies and community clinics, where she has excelled in medication management, patient counseling, and clinical support. Agarwal is known for her expertise in drug therapy optimization and patient safety. In addition to her practical experience, she contributes to health journalism, focusing on pharmaceutical advancements and health policy, and is involved in research projects aimed at improving medication practices and health outcomes. is known for her expertise in drug therapy optimization and patient safety. In addition to her practical experience, she contributes to health journalism, focusing on pharmaceutical advancements and health policy, and is involved in research projects aimed at improving medication practices and health outcomes.