What Are The Common Diagnostic Tests For Heart Attack?
What Are The Common Diagnostic Tests For Heart Attack?
- Is a blood test to detect heart attack necessary?
- Main reasons for performing blood test as part of diagnostic tests for heart attack.
- Are there occasions when blood tests are not carried out as part of diagnostic tests for heart attack?
- Can 2D echo detect heart attack?
- Can ECG detect heart attack?
- Can oximeter detect heart attack?
- What are the primary diagnostic tests for heart attack?
- What is the typical approach to testing?
- What is the percentage of risk of heart conditions from genetic predisposition?
- How to benefit from genetic testing to check risk of heart attack?
- What conditions are linked to risk of heart attack, that can be uncovered by genetic testing?
- Is genetic testing for heart attack risk available in Tamilnadu?
Introduction
Imagine a situation where someone known to you has all the symptoms of a heart attack. If you are not a healthcare professional, you are most likely to either panic or be unaware what needs to be done. The first step is of course to call a hospital for emergency services. Following this, depending on the condition, prescribed medications are to be given, and if trained, you can also give CPR if the patient has lost consciousness or if breathing/pulse has stopped. However, it is important to know about the diagnostic tests for heart attack that the person has to undergo. This will help confirm or rule out a heart attack.
Is a blood test to detect heart attack necessary?
Yes, this is almost always recommended when a person is suspected of having had a heart attack. This is usually performed immediately after an ECG or EKG and is part of the initial diagnostic tests for heart attack. The purpose of a blood test to detect heart attack is mainly to confirm damage to the heart muscle. Typically, there are three types of tests, however, it is always usually the troponin test that is performed by default.
- Troponin test – This is a test that measures the levels of troponin in the blood sample. Troponin is a protein in the heart muscle, and the levels of this protein in the blood are low, when you are normal. However, if there has been some damage to the heart muscle by way of a heart attack, this protein leaks into the bloodstream, and your troponin levels will increase. When damage is severe, more troponin is released in the blood. This test, therefore, helps to estimate the extent of damage to the heart.
Main reasons for performing blood test as part of diagnostic tests for heart attack.
- Better diagnosis to indicate heart muscle damage, through reliable sensitivity to heart muscle injury.
- The high levels of troponin in blood samples will either confirm or rule out a heart attack. For example, angina or gastrointestinal issues are also other possible reasons of chest pain.
- Extent of damage is assessed through the values in the biomarkers, helping determining the severity of the attack.
- Gives a sense of urgency to the treatment by helping specialists decide on the type of treatment required.
- Monitoring outcome of treatment by measuring the biomarkers values in subsequent tests.
Are there occasions when blood tests are not carried out as part of diagnostic tests for heart attack?
Yes, there are specific circumstances, when blood tests are not recommended. For instance, if the patient is known to be very serious condition, requiring CPR or defibrillation, blood tests are skipped. Similarly, if there is a clear clinical diagnosis through ECG findings that confirm a heart, blood tests are skipped.
Can 2D echo detect heart attack?
The answer to this question can only be a nuanced answer, as it is not possible to give a binary answer of yes or no. A 2D echocardiogram helps to assess heart function and also identifies issues that could be related to a heart attack. However, it is always used as a complementary test along with primary diagnostic tests for heart attack. For instance, it is performed along with an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) and blood tests.
Before we look at details, it is necessary to note that an echocardiogram and 2D echo are essentially the same. This is a diagnostic test that relies on ultrasound waves to evaluate the heart’s functioning. The echo from waves relay moving images of the heart and valves onto a monitor. This image is the Echocardiogram, and helps to assess damage due to clots, blockage, or other heart defects.
Can ECG detect heart attack?
Yes, an ECG or electrocardiogram is considered as accurate in diagnosing certain types of heart diseases. However, there are occasions when a person who actually has a condition, will have perfectly normal ECG readings. In such instances, if the treating specialist suspects a heart issue, another ECG or other diagnostic tests for heart attack will be recommended. While the ECG is considered as a primary diagnostic tool, in some cases, you may have to agree to undergo other tests when the results are not conclusive.
How does ECG detect a heart attack?
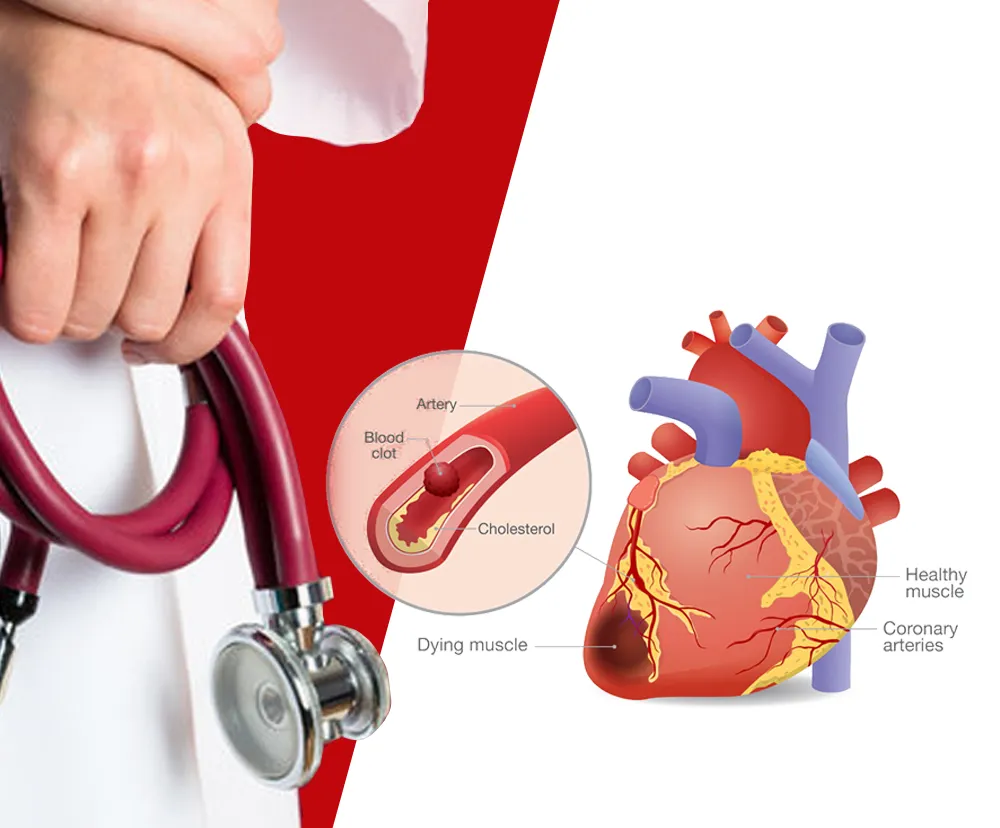
An ECG works by identifying abnormal patterns in the heart muscle. This is done by attaching small electrodes to the arms, leg and chest. These electrodes measure the electrical signals from the heart and print the signals as lines that are interpreted by the specialist. The different abnormal patterns indicate that the heart muscle is not receiving enough oxygen. This could be due to a blocked artery or due to poor blood supply depriving the muscle of oxygen. One abnormal pattern develops much later, and indicates that death of a portion of the heart muscle.
Why is it necessary to opt for other diagnostic tests for heart attack with an ECG?
There are certain limitations of ECG in detecting a heart attack. For example, if you have a heart attack classified as Silent or Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarctions, abnormal patterns will not reflect in an ECG. Another reason is that person may have some existing heart condition or structural defect, and this causes baseline variations. As a result, it makes it difficult to interpret the readings. Additionally, there is also the possibility of the results turning up false positives or false negatives. This is primarily due to other conditions like pericarditis or any imbalance in electrolytes.
Can oximeter detect heart attack?
No, a pulse oximeter can only offer an indirect indication of a possibility of heart attack. It cannot be considered as a reliable tool to detect heart attack. Though it is true that oxygen saturation and heart rate changes during a heart attack, this is not a confirmed indicator. Let’s understand why a pulse oximeter is a part of the diagnostic tests for heart attack, but not a primary tool.
What happens to oxygen levels and pulse during a heart attack?
When you have a heart attack, your blood oxygenation and pulse rate will change. This is because of the damage to the heart muscle, and the ensuing decrease in blood flow. Blood oxygen levels are known to come down below 90% during a heart attack. But this is not the case always. At times, the blood oxygen levels are compensated by the body, and as a result there may be no changes in oxygen levels.
What are the primary diagnostic tests for heart attack?
The primary tests that are usually performed to check for a heart attack include the following. However, it is important to note that it is not always necessary for you to undergo all the tests. The actual tests are determined by the symptoms, the medical history of the patient, and findings from initial assessment.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).
- Blood tests – Troponin, Creatine Kinase-MB, Myoglobin.
- Chest X-ray.
- Echocardiogram.
- Coronary Angiography.
- Cardiac CT or MRI.
- Stress Tests.
- Nuclear Imaging.
What is the typical approach to testing?
Typically, the diagnostic tests for heart attack are carried out in the following sequence or approach.
Step #1 – The patient undergoes an initial assessment through electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), and blood tests to check for troponin levels. The first test is almost always the ECG/EKG, followed by the blood tests.
Step #2 – In the event of the above two tests showing inconclusive results, and if the specialist suspects a heart attack, you will undergo further evaluation. This includes an echocardiogram or coronary angiography. You may also have to get a chest X-ray, mainly to rule out other reasons of chest pain. The X-ray also helps get a clearer picture of the size and shape of the heart.
Step #3 – For in depth details to determine the best treatment option, it will then be necessary to go in for detailed imaging and other functional tests. This includes a cardiac CT, MRI, or nuclear imaging. In addition to these tests, you may also be put through certain tests to check your heart’s functioning when stressed. However, this is applicable only if you are in a stable condition and in a position to undergo some kind of physical exertion.
The sequence and nature of diagnostic tests for heart attack entirely depend upon certain priorities. For example, the diagnostic value of chosen tests, the condition of the patient, and the time available to take a quick decision are all factors. The whole purpose of protocols and a need-based approach is to accurately and swiftly diagnose a heart attack. This will help in extending the right treatment to mitigate possible damage to the heart and ensure better or desired outcomes.
What is the percentage of risk of heart conditions from genetic predisposition?
Four out of ten people who are at risk of heart attack are people who have inherited the condition. As shocking as it may appear, this is the bare fact about genetic predisposition to heart attacks. Some of the main reasons for heart attack are triggered by what is called as the genetic component. This includes hypertension and atherosclerosis.
How to benefit from genetic testing to check risk of heart attack?
With genetic testing it is possible to actually avoid a situation where you will need diagnostic tests for heart attack. Genetic testing offers actionable information on risk of future heart attacks. This is through identification of certain genetic mutations and variations that are clearly linked to heart diseases.
- Identification of genetic variants – Certain single nucleotide polymorphisms and genetic variations are identified as linked to increased risk of heart attack. Variations impact lipid metabolism, blood pressure levels, and specific inflammatory responses.
- Cardiovascular conditions that are passed down the family – Inherited heart conditions predispose people to risk of heart attacks.
- Medications as per different parameters of individuals – Based on the results, it is possible to opt for individualized treatment plans, and changes in lifestyle. These pre-emptive methods can be changed as per the genetic profile of the individual, that varies from person to person. This offers better, nuanced results.
- Screening of family members – Genetic testing is ideal for evaluating risk to other family members when someone in the family has the condition. This helps in early detection and helps in chalking out the right steps for preventing.
What conditions are linked to risk of heart attack, that can be uncovered by genetic testing?
The following conditions are linked to a higher risk of heart attack, and can be detected through genetic testing.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia – This is a genetic disorder where the person has high cholesterol levels, resulting in heart disease. This disorder involves three different genes.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Patients with this condition end up with abnormally thickened heart muscles. This increases the burden on the heart when pumping blood. This disorder also involves three different genes.
- Long QT Syndrome – This is a condition affecting the heart’s electrical activity causing acute, uncontrollable, and life endangering irregular heartbeats. The number of genes involved in this condition are three.
- Marfan syndrome – This refers to a connective tissue disorder that results in the formation of bulges in the artery. Known as aortic aneurysm, this considerably increases the risk of heart attack and involves one gene.
- Brugada syndrome – This condition affects ECG findings, increasing the risk of fatal heart disease. This condition involves one gene.
- Polygenic risk factors – This refers to various genes that contribute to the risk of heart attack, due to the collective effects of the genetic variations. The test calculates the cumulative polygenic risk scores to quantify the risk of heart disease.
Is genetic testing for heart attack risk available in Tamilnadu?
Yes, genetic testing for future risk of heart attack due to genetic factors is presently available in Tamilnadu. The testing protocol and the timeline of the testing, analysis and results are outlined below.
#1 You will undergo pre-test counseling to understand all about the tests, its limitations and its implications.
#2 You will provide a sample of either your blood or saliva for DNA extraction. This takes a few minutes at the maximum.
#3 The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to identify variations in genes. This analysis could sometimes run into a few weeks, between 2 weeks to 6 weeks.
#4 Following the analysis, the healthcare provider explains the outcomes of the results over a single session.
Avoid the future need of undergoing diagnostic tests for heart attack by checking your genetic predisposition. This ensures early intervention, and minimizes your risk of heart ailments, apart from avoiding extended hospitalization and the time for recovery from an attack.
Medically Reviewed by
Dr.Rajasekar Cardiologist
Dr. Rajasekar is a cardiologist in Chennai, with extensive experience in the field. He completed his MBBS from Madurai Kamaraj University, followed by an MD in General Medicine and a DM in Cardiology from The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University (TNMGRMU).
Related Blogs :
Why You Need To Start Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Slide HeadingLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.Click Here Previous Next What is the main information...


Life Saving Tips on how to stop Heart Attack
Introduction How to stop a heart attack in 30 seconds? Why time is of utmost importance? How to stop heart attack if you see signs of it...

Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) from the University of Delhi Experience : Dr. Srinivasan is an experienced pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from the University of Delhi and over 12 years in the field. She has worked extensively in clinical and community pharmacy settings, focusing on patient care, medication management, and drug safety. Dr. Srinivasan also contributes to health and wellness publications and serves as a consultant for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare organizations. Her expertise spans clinical practice, pharmaceutical writing, and regulatory affairs.