Expert suggestions on medical interventions for heart attack prevention
Expert suggestions on medical interventions for heart attack prevention
- What are the medical interventions for heart attack prevention?
- What is the best treatment medicine for heart attack prevention?
- Will heart attack prevention medicine stop a heart attack?
- What is the average cost of treatment of heart attack treatment in India?
- How will genetic testing help detect and prevent a heart attack?
- How is genetic testing for heart attack performed?
Introduction
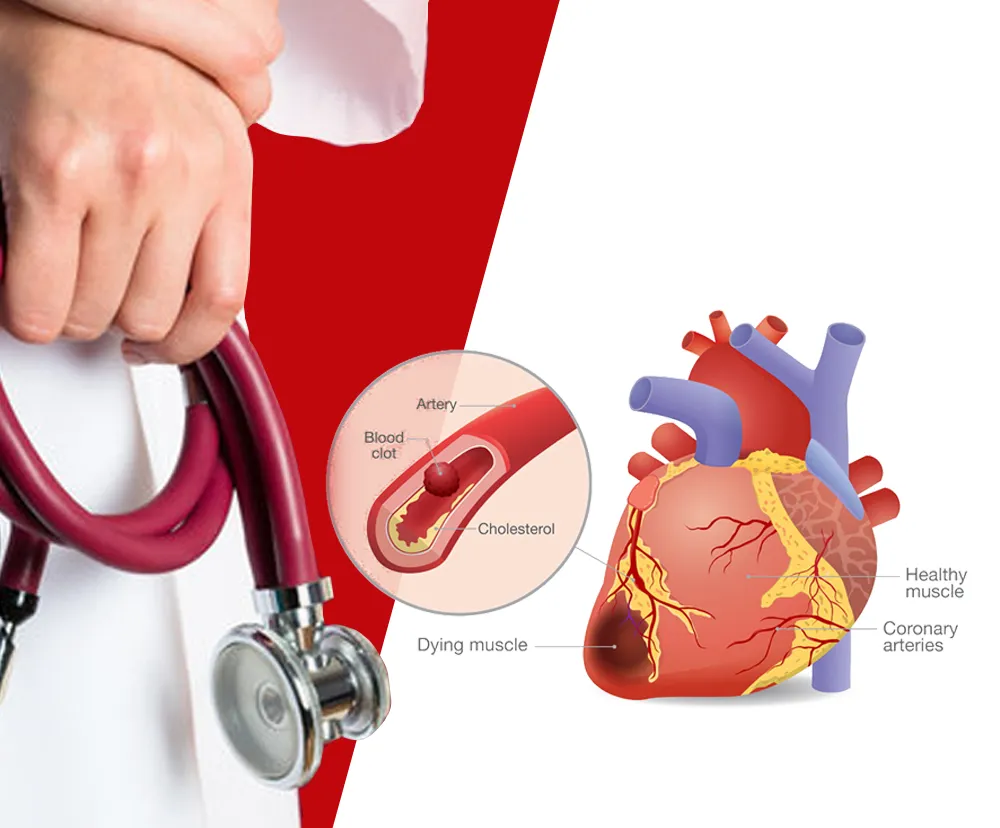
Simple cost comparison between preventing a heart attack and treatment post heart attack clearly add to the benefits of prevention. Depending on the type of treatment required, you may have to fork out as much as four lakhs for a procedure. Regardless of the insurance coverage, you will still have to foot bills. The incomparable benefit of prevention is the possible outcome of a heart attack, the tense moments, the post-attack treatment. It makes sense to follow expert suggestions on medical interventions for heart attack prevention. Here are some of the top strategies compiled for your benefit.
What are the medical interventions for heart attack prevention?
The following interventions can help prevent a heart attack or mitigate the effects of one. A sequence of actions, such as screening, lifestyle modifications, medications, etc. should be followed.
#1. Periodic screening
- Blood tests – Cholesterol, blood sugar, and other markers of heart attack risk.
- Blood pressure – Monitoring blood pressure levels periodically.
- Stress tests and imaging – Stress echocardiograms or CT scans for detailed observation of heart health.
#2. Modifications to lifestyle
- Diet – A heart-healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise – Regular exercise, with a minimum of two and a half hours per week of moderate-intensity activity.
- Weight – Achieving and maintaining the right weight to reduce the workload on the heart.
- Smoking – Ceasing smoking completely to improve heart health.
- Alcohol – Regulating alcohol intake, or if possible, stopping intake completely.
#3. Medicines
- Antiplatelets – Aspirin and clopidogrel to prevent blood clots.
- Statins – Atorvastatin and simvastatin to bring down cholesterol levels.
- Beta-Blockers – To reduce blood pressure levels and heart rate, which help to reduce the burden on the heart.
- ACE inhibitors/ARBs – Enalapril and losartan to bring down blood pressure levels.
- Diuretics – To control blood pressure levels by bringing down fluid retention.
- Nitroglycerin – To offer relief from chest pain, also known as angina.
#4. Procedures
- Angioplasty, stenting: To widen or open up narrowed/blocked coronary arteries, followed by positioning a stent.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting – To create a new pathway to facilitate blood flow to the heart.
#5. Treating underlying conditions
- Hypertension – Regulating high blood pressure levels to desired levels.
- Diabetes – Ensuring healthy blood sugar levels.
- Cholesterol – Controlling cholesterol levels through medications.
#6. New treatment regimen
- PCSK9 inhibitors – New drug formulations to reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
- Anticoagulants – To manage risk of blood clot formation.
- Wearables – Technology to monitor heart health and trigger notifications.
What is the best treatment medicine for heart attack prevention?
Different medications are recommended as treatment post heart attack and for preventing a heart attack among high risk patients. It is difficult to claim that a single medication is the best medical interventions for heart attack prevention. Here are some of the medications that are commonly used as part of treatment regimen.
- Antiplatelets – These drugs are also known as blood thinners, and reduce the risk of blood clots. One of the most common medications of this category is Aspirin, and it is mostly combined with clopidogrel.
- Fibrates – To lower high cholesterol levels, indirectly reducing your risk of heart attack.
- Statins – To lower cholesterol and other fats in your body, indirectly reducing your risk of heart attack. Commonly prescribed statins include atorvastatin, pravastatin, and simvastatin.
- ACE inhibitors – To treat heart failure and lower blood pressure, lowering your risk of heart attack, if you are diagnosed with coronary artery disease.
- Diuretics – To facilitate removal of sodium and water from the kidneys, and to relax blood vessel walls. This, in turn helps reduce your blood pressure.
- SGLT2 inhibitors – To reduce the risk of heart attack if you are identified as high risk.
Will heart attack prevention medicine stop a heart attack?
Three categories of medicines are usually prescribed to help prevent a heart attack when a patient is diagnosed as high risk. These are antihypertensives, statins and antiplatelets. These medications will considerably lower the risk of heart attack, but, only if combined with other recommendations. For example, medical interventions for heart attack prevention include lifestyle changes, drastic diet modifications, and periodic check-up or monitoring of health. The underlying conditions that are responsible for the risk are to be treated.
What is the average cost of treatment of heart attack treatment in India?
The cost of various treatments may differ, depending on the hospital, the location and the supportive care. However, the average costs may be listed as follows:
- Open heart surgery – ₹1.75 lakh to ₹4.25 lakh
- Coronary angiography – ₹10,000 to ₹15,000
- Valve surgeries – ₹2.5 lakh to ₹4 lakh
- Heart bypass surgery – ₹150,000 to ₹400,000
- Coronary angioplasty, stenting – ₹100,000 to ₹300,000
How will genetic testing help detect and prevent a heart attack?
Genetic testing can help detect and prevent heart attacks by identifying the risks through specific genetic mutations or inherited risk factors. When you are aware of the genetic component of a possible risk, you can seek and receive medical interventions for heart attack prevention. Genetic testing facilities are presently available in Tamilnadu and these advanced lab tests offer a clear prediction of your risk. The tests are relatively simple and painless, with very little time for the sample collection.
How is genetic testing for heart attack performed?
- Sample collection – A simple saliva sample or a cheek swab, or a blood sample may be collected for comprehensive genetic analysis.
- DNA extraction – The sample is processed at a laboratory where the DNA is extracted from the cells in the saliva, cheek swab, or blood.
- Genotyping or Sequencing – Specific locations in the genome are examined for variations that are linked to heart disease. Sequencing refers to a more comprehensive analysis to identify rare variants.
- Analysis – The data is analysed with advanced computational tools to identify variants. Polygenic Risk Scores offer a more comprehensive risk assessment by summing up the effects of multiple genetic variants.
- Reports – The results are interpreted along with the patient’s medical history, family history, and other assessed risks. This gives a detailed report interpreting the identified genetic variants, its impact on the risk, and the recommendations for managing the condition.
Medically Reviewed by
Dr.Rajasekar Cardiologist
Dr. Rajasekar is a cardiologist in Chennai, with extensive experience in the field. He completed his MBBS from Madurai Kamaraj University, followed by an MD in General Medicine and a DM in Cardiology from The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University (TNMGRMU).
Related Blogs :
Why You Need To Start Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Slide HeadingLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.Click Here Previous Next What is the main information...


Life Saving Tips on how to stop Heart Attack
Introduction How to stop a heart attack in 30 seconds? Why time is of utmost importance? How to stop heart attack if you see signs of it...

Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) from the University of Delhi Experience : Dr. Srinivasan is an experienced pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from the University of Delhi and over 12 years in the field. She has worked extensively in clinical and community pharmacy settings, focusing on patient care, medication management, and drug safety. Dr. Srinivasan also contributes to health and wellness publications and serves as a consultant for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare organizations. Her expertise spans clinical practice, pharmaceutical writing, and regulatory affairs.