

What Whole Genome Sequencing Is
- Understanding the Human Genome
- What Is Whole Genome Sequencing?
- How Whole Genome Sequencing Works
- Whole Genome Sequencing vs Other Genetic Tests
- Why Whole Genome Sequencing Matters
- The Role of Genetic Testing in Modern Healthcare
- Conditions and Traits Explored Through WGS
- Accuracy and Reliability of Whole Genome Sequencing
- Who Can Benefit From Whole Genome Sequencing?
- Limitations to Understand
- The Future of Whole Genome Sequencing
- LifeCode and Advanced Genetic Testing
- LifeCode Advanced Genetic Testing
Whole Genome Sequencing, often called WGS, is one of the most complete ways to understand human DNA. It looks at almost every part of a person’s genetic code, giving deep insight into health, inherited traits, and disease risk. As genetic science advances, WGS is becoming a key tool in preventive and personalized healthcare.
This guide explains what whole genome sequencing is, how it works, why it matters, and how it supports modern genetic testing, including advanced panels offered by LifeCode.
Understanding the Human Genome
The human genome is made up of about 3 billion DNA base pairs. These base pairs form genes that guide how the body grows, repairs itself, and responds to the environment.
According to Wikipedia, the human genome contains approximately 20,000 to 21,000 protein-coding genes, along with large regions that regulate how those genes function. These regulatory areas are just as important as genes themselves.
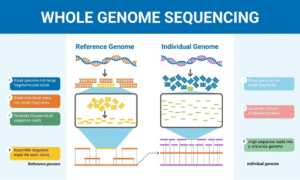
Whole Genome Sequencing reads nearly all of this information in one test.
What Is Whole Genome Sequencing?
Whole Genome Sequencing is a laboratory process that analyzes almost 100% of a person’s DNA. Unlike targeted or partial tests, WGS does not focus on only selected genes. Instead, it captures the complete genetic blueprint.
In simple terms:
- It scans all chromosomes
- It reads coding and non-coding regions
- It identifies millions of genetic variants in one test
Wikipedia describes whole genome sequencing as a method that determines “the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome at a single time,” highlighting its depth and accuracy.
How Whole Genome Sequencing Works
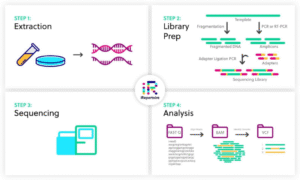
Although the science behind WGS is advanced, the steps are straightforward.
Step-by-step overview:
- Sample collection
A saliva or cheek swab sample is collected. No needles are required.
- DNA extraction
DNA is isolated from the sample in a laboratory.
- Sequencing
Advanced machines read billions of DNA letters using next-generation sequencing technology.
- Data analysis
Powerful software compares the DNA sequence to reference genomes.
- Report generation
Results are organized into clear, meaningful health insights.
Modern sequencing can analyze a full genome in days instead of years, a major improvement compared to early genetic research.
Whole Genome Sequencing vs Other Genetic Tests
Not all genetic tests provide the same level of detail.
Comparison overview:
- Single-gene testing
Looks at one gene only, often for a known condition.
- Targeted panel testing
Examines a selected group of genes related to a specific health area.
- Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
Studies only protein-coding genes, about 1–2% of DNA.
- Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
Analyzes nearly all DNA, including regulatory regions.
WGS offers the most complete genetic picture, making it especially valuable for long-term health planning.
Why Whole Genome Sequencing Matters
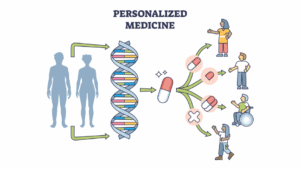
Whole Genome Sequencing goes beyond diagnosis. It helps people understand risk, resilience, and response.
Key benefits include:
- Early identification of inherited disease risks
- Insight into how genes may affect metabolism and nutrition
- Understanding how the body processes medications
- Support for preventive healthcare decisions
- A lifelong resource, since DNA never changes
Large population studies show that most people carry several genetic variants that can influence health under certain conditions. WGS helps identify these early.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Modern Healthcare
Genetic Testing Focus – Required Section
Genetic testing plays a growing role in healthcare by shifting focus from treatment to prevention and personalization.
With Whole Genome Sequencing, genetic testing can:
- Identify risks before symptoms appear
- Support lifestyle and dietary planning
- Help guide discussions with healthcare providers
- Provide clarity when family history is unclear
Wikipedia notes that genetic testing is used to “confirm or rule out suspected genetic conditions” and increasingly to assess predisposition to complex diseases.
LifeCode builds on this foundation by translating complex genetic data into clear, actionable insights.
Conditions and Traits Explored Through WGS
Whole Genome Sequencing can support insights across many health areas.
Common focus areas include:
- Heart and Metabolic Health
- Neurological and cognitive traits
- Immune system function
- Hormone balance
- Fitness and recovery
- Nutrient absorption
- Rare genetic conditions
It is important to note that WGS does not predict certainty. It highlights tendencies and risks, which can often be managed with informed choices.
Accuracy and Reliability of Whole Genome Sequencing
Modern sequencing technologies are highly accurate.
Key data points:
- Sequencing accuracy often exceeds 99.9%
- Millions of variants can be detected in one test
- Results improve as scientific databases grow
According to Wikipedia, advances in sequencing technology have significantly reduced errors and costs, making WGS more accessible and reliable than ever before.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Genetic data is deeply personal. Responsible testing providers focus on:
- Secure data storage
- Transparent consent
- Clear data ownership policies
- Ethical use of genetic information
LifeCode follows strict data protection standards so individuals remain in control of their genetic information.
Who Can Benefit From Whole Genome Sequencing?
WGS is not only for people with known health conditions.
It can be useful for:
- Individuals interested in preventive health
- Families with unclear medical history
- Couples planning for future children
- Athletes optimizing performance and recovery
- People seeking deeper insight beyond basic tests
Because DNA remains constant, one test can provide value for a lifetime.
Limitations to Understand
While powerful, WGS has limits.
- Not all genetic variants have known meanings yet
- Results should not replace medical diagnosis
- Environment and lifestyle still play major roles in health
Whole Genome Sequencing works best when combined with professional interpretation and personalized guidance.
The Future of Whole Genome Sequencing
The future of WGS is closely tied to artificial intelligence and expanding global research. As more genomes are studied, interpretations become clearer and more precise.
Experts expect whole genome sequencing to become a routine part of preventive healthcare in the coming years.
LifeCode and Advanced Genetic Testing
LifeCode uses advanced genetic science to turn complex genome data into clear, human-friendly insights. Rather than overwhelming users with raw data, LifeCode focuses on understanding how genes interact with daily life.
LifeCode’s approach includes:
- Advanced genetic testing panels
- Clear risk interpretation
- Action-oriented insights
- Ongoing education and support
Learn more or get help at lifecode.life.
LifeCode Advanced Genetic Testing
Your DNA holds powerful information about your health, potential, and future choices. Whole Genome Sequencing helps unlock that information in a meaningful way.
Take the next step with LifeCode:
- Book a genetic consultation to understand your results clearly
- Order a genetic testing kit (simple swab test) from home
Explore how advanced genetic testing can support smarter, more informed health decisions with LifeCode.
Get started today at lifecode.life.

What Whole Genome Sequencing Is
What Whole Genome Sequencing Is Understanding the Human Genome What Is Whole Genome Sequencing? How Whole Genome Sequencing Works Whole Genome Sequencing vs Other Genetic Tests Why...

What Targeted Panel Genetic Testing Is
What Genetic Penetrance Means Understanding the Basics of Targeted Panel Genetic Testing How Targeted Panel Testing Works Why Targeted Panels Are Used Instead of Broad Testing Conditions...



