
How Gene Expression Works?
- What Are Genes?
- What Is Gene Expression?
- The Two Main Steps of Gene Expression
- Why Gene Expression Matters for Health
- Gene Expression and Epigenetics
- Genetic Differences and Gene Expression
- Genetic Testing Focus: Understanding Your Gene Expression
- Gene Expression and Lifestyle Choices
- The Future of Gene Expression Research
- LifeCode Panel: Advanced Genetic Testing
- Take Control of Your Genetic Health
Gene expression is the process that turns information in your genes into action. It tells your body when to make proteins, how much to make, and where to use them. These proteins help build cells, repair tissues, and support daily health. Understanding gene expression can help people make better choices about lifestyle, nutrition, and medical care.
Scientists estimate that humans have about 20,000 protein‑coding genes, according to information summarized on Wikipedia. Yet, not all genes are active at the same time. Gene expression decides which genes are “on” or “off,” helping each cell do its job.
What Are Genes?
Genes are small sections of DNA. DNA is the instruction book inside almost every cell. Each gene holds a recipe for making a specific protein.
Key points:
DNA is stored in the cell nucleus.
Genes are made of DNA.
Proteins do most of the work in the body.
Wikipedia explains that DNA uses four chemical bases—adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G)—to store information. The order of these bases forms genetic instructions.
What Is Gene Expression?
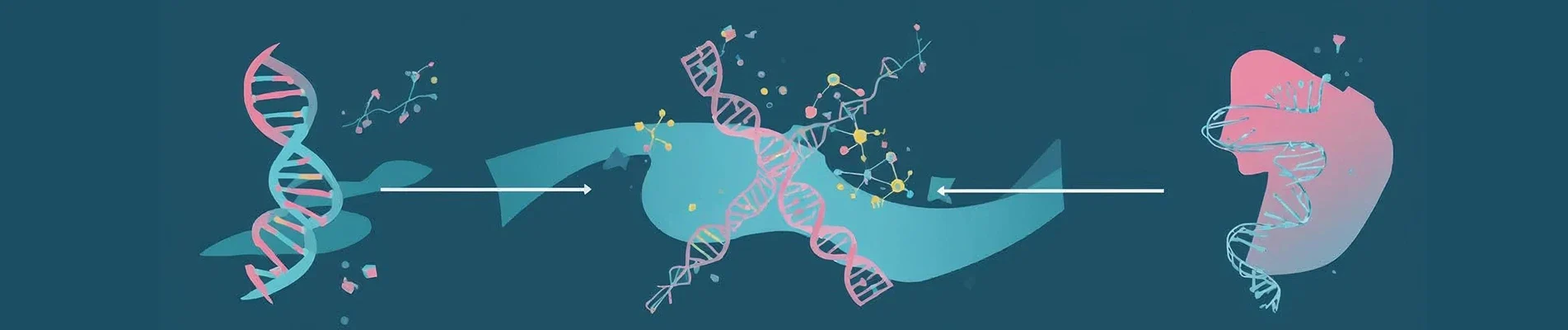
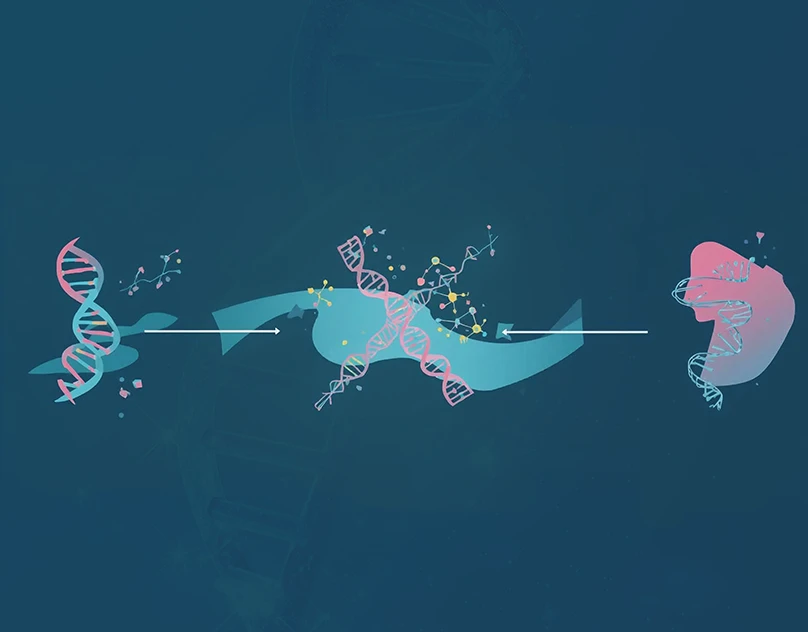
Gene expression is the step‑by‑step process where a gene’s instructions are used to make a protein.
In simple terms:
A gene is read.
A message is created.
A protein is built.
Not all genes are active all the time. For example, liver cells express genes needed for detox, while muscle cells express genes for movement. This is why cells can be different even though they share the same DNA.
The Two Main Steps of Gene Expression
Transcription
Transcription is the first step. During transcription:
This happens inside the nucleus.
Wikipedia notes that RNA is similar to DNA but uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). This small change allows RNA to carry messages.
Translation
Translation is the second step. During translation:
The mRNA travels to a structure called the ribosome.
The ribosome reads the message.
Proteins then fold into shapes that allow them to work correctly.
Why Gene Expression Matters for Health
Gene expression affects almost every part of health, including:
Growth and development
Immune response
Energy production
Brain function
Changes in gene expression can increase the risk of disease. Research shared on Wikipedia explains that many chronic conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, are linked to changes in how genes are expressed rather than changes in the genes themselves.
Studies suggest that the environment and lifestyle can influence gene expression. Factors include:
Diet
Physical activity
Stress levels
Sleep quality
Exposure to toxins
This field of study is often called epigenetics.
Gene Expression and Epigenetics
Epigenetics look at changes that affect gene activity without changing the DNA sequence.
According to Wikipedia, epigenetic changes can:
Turn genes on or off
Be influenced by lifestyle and environment
Sometimes be passed to future generations
Common epigenetic factors include:
DNA methylation
Histone modification
These processes help explain why healthy habits can support better gene expression over time.
Genetic Differences and Gene Expression
Each person’s DNA is slightly different. These differences can affect how genes are expressed.
Examples include:
How the body processes nutrients
How it responds to medications
How it handles stress
Statistics often cited in genetics research show that 99.9% of human DNA is the same, but the small remaining differences can still have meaningful health effects.
Genetic Testing Focus: Understanding Your Gene Expression
The Role of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing helps identify variations in your DNA that may influence gene expression. These tests do not change your genes, but they provide useful information.
Genetic testing can help:
Identify health risks early
Understand how your body processes vitamins and minerals
Guide personalized nutrition and lifestyle plans
Support better medication choices
Wikipedia explains that modern genetic tests often use simple samples, such as saliva or cheek swabs, making them easy and non‑invasive.
How Genetic Testing Supports Prevention
By understanding your genetic profile, healthcare providers can:
Focus on prevention instead of reaction
Recommend targeted lifestyle changes
Monitor areas of higher genetic risk
This personalized approach supports long‑term wellness and informed decision‑making.
Gene Expression and Lifestyle Choices
Your daily habits can influence gene expression in positive ways.
Healthy actions that support balanced gene expression include:
Eating whole, nutrient‑rich foods
Regular physical activity
Managing stress through relaxation or mindfulness
Getting enough sleep
Avoiding smoking and excess alcohol
Research summarized on Wikipedia highlights that lifestyle changes can lead to measurable epigenetic improvements, even within weeks or months.
The Future of Gene Expression Research
Advances in science continue to improve our understanding of gene expression. Areas of growth include:
Personalized medicine
Targeted nutrition plans
Early disease detection
Experts believe that gene‑based care will become a key part of preventive health in the coming years.
LifeCode Panel: Advanced Genetic Testing
LifeCode helps individuals understand how their genes work for them, not against them. Through LifeCode Panel Advanced Genetic Testing, users gain clear insights into genetic factors that affect health, wellness, and daily performance.
LifeCode focuses on:
Easy‑to‑understand results
Practical health guidance
Support for long‑term wellness goals
Learn more at https://lifecode.life.
Take Control of Your Genetic Health
Understanding how gene expression works is the first step toward better health. The next step is action.
With LifeCode, you can:
Book a genetic consultation with trained professionals
Order a genetic testing kit (simple swab test) from the comfort of your home
Discover how your genes support your health journey and make informed choices for the future.
Visit https://lifecode.life today and start your personalized genetic wellness plan.

What Longevity Genetics Means
What Whole Genome Sequencing Is Understanding the Human Genome What Is Whole Genome Sequencing? How Whole Genome Sequencing Works Whole Genome Sequencing vs Other Genetic Tests Why...


What Whole Genome Sequencing Is
What Whole Genome Sequencing Is Understanding the Human Genome What Is Whole Genome Sequencing? How Whole Genome Sequencing Works Whole Genome Sequencing vs Other Genetic Tests Why...