Acute myeloid leukemia treatment
Acute myeloid leukemia treatment
Introduction
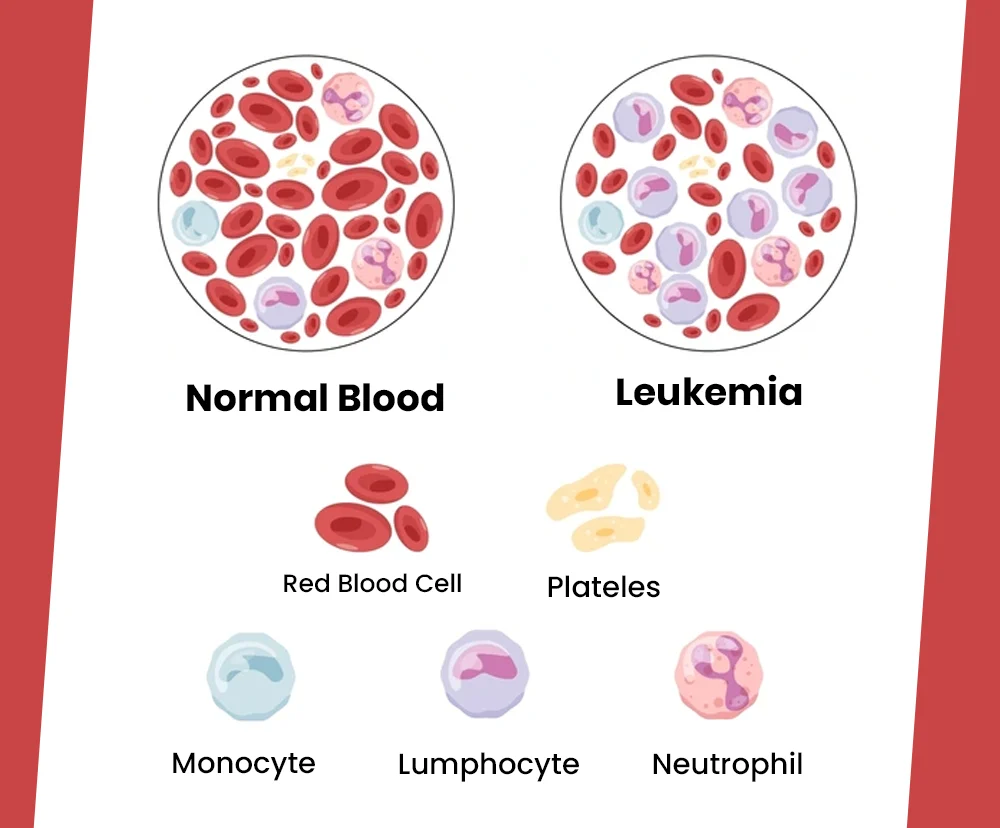
Myeloid is a tissue of your bone marrow. These are essentially blood cells. Acute myeloid leukemia is a cancerous condition of myeloid genre of blood cells. When such cells witness faster growth, they interfere with other unaffected cells of your blood. In some rare cases, this type of cancer may spread to your skin, brain or oral parts. The spreading process occurs in a rapid fashion; hence, if you are not treating this, it may turn into a fatal condition in a few weeks’ time.
Factors that are considered as risks include being a male, smoking of tobacco products, turning older, working in an environment that has risks of exposure to benzene, prior sessions of radiation therapy or chemotherapy sittings. This condition witnesses leukemia-cells slowly replacing healthier cells of your bone marrow. As a result, you may experience a sudden decrease in white cells and red cells of your blood. As a parallel development, the number of platelets may also come down.
Leukemia signs and symptoms
The typical signs and symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia are being fatigued or tired, respiratory conditions like gasping for breath or panting, internal bleeding or development of bruises. In most cases, you may turn vulnerable to infectious conditions; this is chiefly due to the drop in number of white cells in your blood.
You can also identify a decrease in red cells by a few of its characteristic signs; these are palpitations, rapid heart rate coupled with sweating profusely, episodes of extreme fatigue, turning pale and increase in respiratory rate. Drop in count of platelets can cause traces of blood from your nasal passages, bruising more frequently and bleeding easily.
Your spleen is likely to get enlarged owing to the incidence of acute myeloid leukemia. But often times, this is asymptomatic and also very mild. On the other hand, inflammation of lymph nodes is not a common occurrence. A few people living with acute myeloid leukemia may witness inflammation of their gums; this is mainly due to leukemia cells gaining entry inside tissues of your gums.
Some rare symptoms involve the respiratory tract as well as the gastric system; but these are uncommon symptoms. Treatment modality stand influenced by another symptom; this is the impact acute myeloid leukemia causes to the meninges of your central nervous system (CNS).
Risk factors of acute myeloid leukemia are sittings of chemotherapy – especially being exposed to alkylating agent of the antineoplastic sub-genre. A few other chemo drugs such as topoisomerase-II inhibiting meds as well as meds like fludarabine.
People who have been administered with these drugs may get acute myeloid leukemia after a few years. In case of the former, risks may emerge within 3 years from the time of dosing; for the latter, acute myeloid leukemia can show up after a span of 5 years’ time.
High-energy and high-focus radiations of the ionising kind – administered to treat a few other types of cancers – may enhance the risks of acute myeloid leukemia. Those who were exposed to ionised rays to treat breast cancers, prostate cancers, lung cancers, lymphoma of the non-Hodgkin type, etc. are at an added risk of getting acute myeloid leukemia.
In general, those who have a high body mass index (BMI) – of more than 27 – are at risk of being affected by acute myeloid leukemia. The risk levels are the same as that of smoking tobacco-based products.
Also, if you are working in the nuclear power sector or manufacturing of computer goods or electronic items, the risks are more pronounced. You are equally exposed to acute myeloid leukemia risks if you are employed in the animal slaughter trade or fishing as well as processing of meat products.
Acute myeloid leukemia medical procedure
Different approaches exist for treating acute myeloid leukemia. Your oncologist chooses an approach based on your medical condition, age and onset of prior ailments, if any. The various approaches include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, chemo with stem-cell transplants, and a few other forms of drug-based therapies.
Not stopping with these, newer forms of treatment modalities are under testing stage. Regardless of the approach taken to treat acute myeloid leukemia, you are likely to witness a few adverse effects. Hence, follow-up procedures are commonly embedded as part of treatment plans to manage acute myeloid leukemia.
On the whole, Acute myeloid leukemia treatment involves two distinctive stages: remission and post-remission. Of these two stages, the former is the first stage of treatment offered to this form of cancer. Here, the focus is to destroy cells of leukemia; treatment is aimed at bone marrow as well as blood. The primary objective is to put your cancerous condition into a stage of remission.
Post-remission stage is the second stage of treating this form of leukemia. This is however started only after leukemia is on its remission mode. Here, the aim is to terminate cancerous cells that are still alive – i.e., after the above phase of treatment. Goal is to kill cells that were not very active during the early phase, but have starting growing. This stage of treatment is also labelled as remission continuation therapy.
Patients who undertake the abovementioned treatment protocols to manage acute myeloid leukemia must be under closer watch. This is mainly due to a condition called myelo-suppression; this shows up through a sizable drop in red cells, white cells as well as platelets in your blood. Supportive treatment involves transfusions to replace platelets and red cells of blood. As a parallel support measure, administration of antifungals as well as antibiotics is started to fight off infectious conditions (triggered due to a fall in the number of white cells)
Radiation therapy for acute myeloid leukemia
This approach uses x-rays of very high energy onto the affected site. These rays either kill cancerous cells or arrest them from growing any further. In case of acute myeloid leukemia, this therapy is offered through the external mode. This is done by using a device external to your body; it transmits x-rays to the site where cancer cells grow rapidly.
Another popular technique is irradiation of your entire body. Here, x-rays are sent all over your system. This is widely pursued prior to transplantation of stem cells – especially, when there is a relapse of leukemia.
Chemo drugs with stem cell transplantation for treating acute myeloid leukemia
Often, healthier / normal cells are killed as part of cancer care. Stem cell transplantation aims to replace the blood cells with immature / younger blood cells. Such blood-creating cells – of the younger type – are carefully removed from the marrow or blood. These are stored in very low / freezing temperatures.
One you have completed procedures of irradiation of full body or chemo sittings, stem cells that are frozen are thawed. These cells are then transplanted into your system through a procedure called infusion. Once infused, these new cells will mature and help restore the loss of blood cells
Leukemia medication / use of chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia
Here, drugs are used to arrest the rapid growth of tumor-causing cells. These drugs either focus on stalling cancerous cells from multiplying or kill them. Approach to chemotherapy is decided by the type of acute myeloid leukemia you are affected by. Also, if the cells have spread to nerves of your nervous system determines the intensity of chemo treatment.
Meds used for treating acute myeloid leukemia are mitoxantrone, cytarabine, decitabine, etc. In most cases, these drugs are administered in a combinatorial form. If leukemia has spread to nerves, drugs are injected to the spinal column. This helps to breach the brain-blood barrier; this may prevent drugs from gaining access to your central nervous system.
Of the many drugs used under the banner of chemotherapy, methotrexate and cytarabine are widely used through the intrathecal route i.e., delivered via your spinal column
Acute myeloid leukemia survival rate
The diagnosis of conditions like acute myeloid leukemia can be quite frightening. This is because as low of ~ 30.8% of those who get this form of leukemia will survive for more than 5 years. However, rates of survival depend on many factors viz., your age, biological nature of the condition, etc. Good news for those less than 20 years of age: survival rate of acute myeloid leukemia among this age group is more than 65%.
In general, the younger a person is – the better are the chances of surviving acute myeloid leukemia. On the other hand, people aged above 60 years are known to have very low rates of survival. In fact, this is the age group that sees a high % of mortality than all other age groups
Related Blogs :

Leukemia Blood Test
Leukemia Blood Test Introduction Blood test for leukemia Leukemia diagnosis blood test Leukemia blood test results Leukemia cancer CBC blood test results Leukemia positive cancer blood test...

Chronic myeloid leukemia
Chronic myeloid leukemia Introduction Chronic myeloid leukemia ICD 10 What is chronic myeloid leukemia? Chronic myeloid leukemia symptoms Chronic myeloid leukemia treatment Introduction Tissues of the marrow...

Dr. Srinivasan is a cardiologist in Chennai, with extensive experience in the field. He completed his MBBS from Madurai Kamaraj University, followed by an MD in General Medicine and a DM in Cardiology from The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University (TNMGRMU).